Chapter: Introduction to Main Parts of a Computer
This chapter provides information about the main components of a computer and focuses on their roles. It mainly describes four core parts: Central Processing Unit (CPU), Memory, Input Devices, and Output Devices.
The CPU, known as the brain of the computer, is responsible for processing data and making decisions. Memory, which includes RAM and ROM, is responsible for storing and accessing data. Input devices, like the keyboard and mouse, help users interact with the computer, while output devices, such as the monitor and printer, display the processed data.
This chapter also explains how all these components work together so that the computer can operate in a smooth and efficient manner.
Hardware (Input/Output Devices, CPU, Memory)
Computer hardware refers to the physical parts that make up a computer system. These include several key components such as:
1. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Often called the brain of the computer, the CPU is responsible for executing instructions and processing data. It performs calculations and manages tasks by interpreting and executing program instructions.

2. Memory
- Random-Access Memory (RAM): A type of volatile memory used to store data actively being processed. RAM allows fast access and enhances performance.
- Storage Devices: Such as Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Solid-State Drives (SSDs), essential for long-term data and program storage.
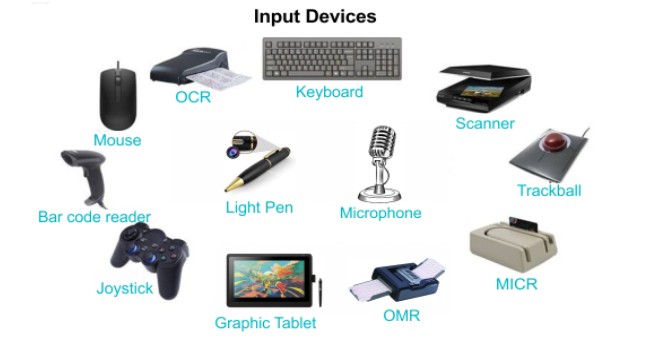
3. Input Devices
Hardware components that allow users to input data into the computer. Examples:
- Keyboard
- Mouse
- Scanner
- Microphone
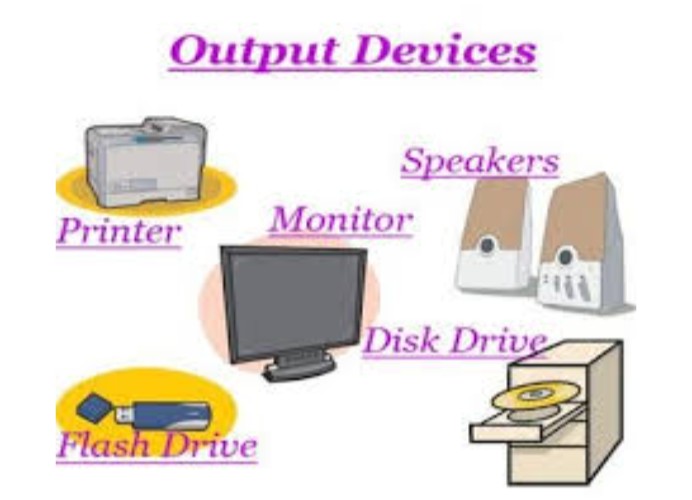
4. Output Devices
Devices that deliver information from the computer to the user. Examples:
- Monitor: Displays visual output
- Printer: Produces physical documents
- Speakers: Output audio
Software (System Software, Application Software)
Software can be divided into two main categories: System Software and Application Software.
1. System Software
Designed to manage hardware and provide a platform for application software. Includes:
- Operating Systems (e.g., Windows, macOS, Linux)
- Device Drivers
- Utility Programs

2. Application Software
Developed for specific user tasks. Examples:
- Word processors (e.g., MS Word)
- Spreadsheets (e.g., Excel)
- Web browsers (e.g., Chrome)
- Media players, graphic design software, etc.

System software enables and supports the application software that directly interacts with the user.
Data and Interface
Data
Data refers to the information processed or stored by a computer, in forms like text, numbers, images, etc. It's the foundation for computation and output.
Interface
An interface is the point of communication between different components. It ensures proper data exchange and functioning.
Types of Interfaces:
- User Interface (UI): Interaction point between user and system (e.g., GUI, CLI).
- Application Programming Interface (API): Rules and protocols for software components to communicate.