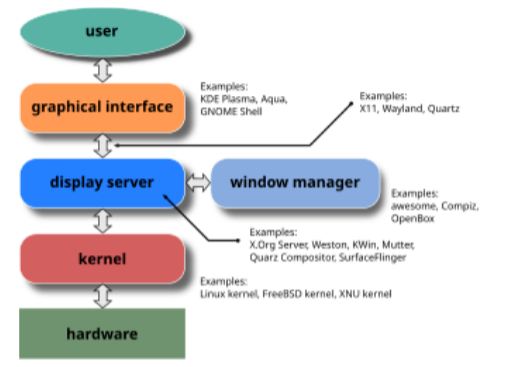
This chapter provides detailed information about the history and development of computers. It begins with ancient tools like the abacus and Pascaline, which laid the foundation of computing. In the 19th century, Charles Babbage's Analytical Engine paved the way for modern computers. The 20th century saw the era of electronic computers such as ENIAC and UNIVAC, which were based on vacuum tubes. The invention of transistors and integrated circuits made computers smaller, faster, and more powerful. The 1970s and 1980s witnessed the emergence of personal computers (PCs), led by companies like Apple and IBM. The internet revolution of the 1990s transformed the world. Today, new developments like quantum computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud technology are reshaping the future of computing.
Generations of Computers:
- First Generation (1940-1956): Computers based on vacuum tubes were large, expensive, and consumed a lot of electricity. Examples: ENIAC, UNIVAC.
- Second Generation (1956-1963): Transistors replaced vacuum tubes, making computers smaller, faster, and more reliable. Languages like COBOL and FORTRAN were introduced.
- Third Generation (1964-1971): Integrated Circuits (ICs) emerged, allowing multiple transistors on a single chip. This reduced size and cost while improving performance. Operating systems became smarter enabling multitasking.
- Fourth Generation (1971-Present): Marked by microprocessors, leading to the development of personal computers. Rapid advances included the internet and mobile computing.
- Fifth Generation (Present and Beyond): Focused on AI and machine learning, aiming to create systems that can learn, reason, and self-improve. Research into quantum computing is ongoing.





Important Milestones:
- Abacus: One of the oldest calculation tools using beads on rods, laying the foundation for future computational devices.
- Analytical Engine: Designed by Charles Babbage in the 1830s, considered the first concept of a general-purpose computer.
- Turing Machine: Proposed by Alan Turing in 1936, a theoretical model defining the limits of computation, influencing algorithms and programming.



The development of modern computers includes milestones like microprocessors, graphical user interfaces (GUIs), the internet, mobile computing, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence.

- Microprocessor: Introduced in the early 1970s, microprocessors revolutionized computing by integrating all processing functions into a single chip, leading to the spread of personal computers.
- Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs): The introduction of GUIs in the 1980s made computers more accessible to the general public by allowing easier interaction through visual elements instead of text-based commands.
- Networking and Internet: In the 1990s, the advent of networking technologies and the World Wide Web changed the way computers communicate, creating a connected world as we know it today.
- Mobile Computing: The rise of smartphones and tablets in the 2000s made computing portable, enabling users to access information and work on the go.
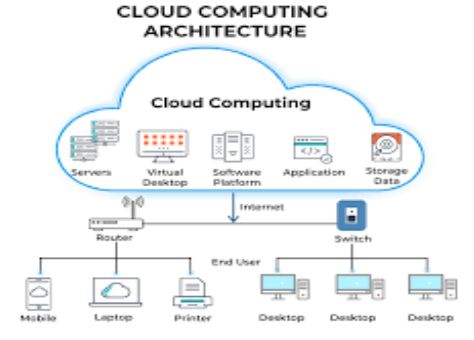
- Cloud Computing: Emerging in the late 2000s, cloud computing enables data storage and processing over the Internet, providing scalability and flexibility for users and businesses.
- Artificial Intelligence: Recent advances in AI and machine learning are driving innovation across various fields—from healthcare to finance—shaping the future of computing with smart applications and systems.