Types of computers is an important topic widely used in the world of technology. In this chapter, we will classify computers into different categories such as personal computers, laptops, servers, and mobile devices. Each type has its own features and uses, which are important in the context of their usage. For example, personal computers are generally used for home or office work, whereas servers are made to provide services to dozens of users. In this chapter, we will also discuss the construction, functions, and uses of each type of computer, which will help students understand the prevalence of computers and their development.
Based on Size and Capacity (Supercomputer, Mainframe, Microcomputer)
Computers can be categorized into various types based on their size and data handling capabilities. Below is the description of the main types:
- Supercomputer:
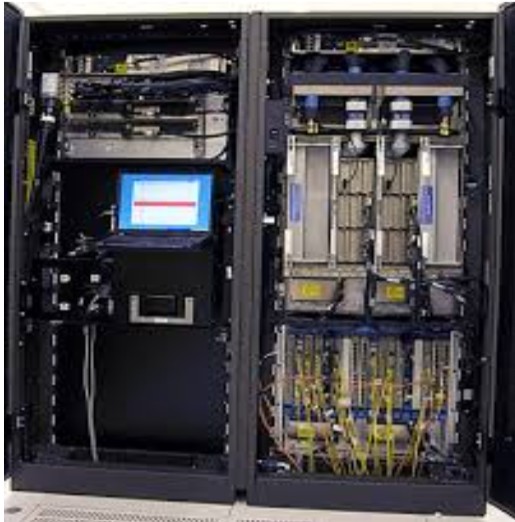
- Size and Capacity: Supercomputers are the largest and most powerful type of computers. They are designed to perform very complex calculations at extremely high speeds, often measured in petaflops (quadrillions of calculations per second).
- Usage: They are generally used for scientific simulations, weather forecasting, climate research, nuclear modeling, and other tasks that require huge computational power. - Mainframe Computer:
- Size and Capacity: Mainframes are large, powerful machines capable of handling massive amounts of data simultaneously. They are smaller than supercomputers but larger than microcomputers and can process millions of transactions per second.
- Usage: Mainframes are typically used by large organizations for bulk data processing, transaction processing, and resource management. They are known for their reliability and security. - Mini Computer:
- Size and Capacity: Mini computers, also called mid-range computers, are smaller than mainframes but larger than microcomputers. They can support multiple users simultaneously and handle moderate workloads.
- Usage: They are used in small to medium-sized businesses for database management, scientific applications, and industrial control systems. - Microcomputer:
- Size and Capacity: Microcomputers, also known as personal computers (PCs), are the smallest category of computers. They typically use a single microprocessor and are designed for individual use.
- Usage: Used commonly in homes and offices, microcomputers are suitable for word processing, web browsing, gaming, and general-purpose tasks.



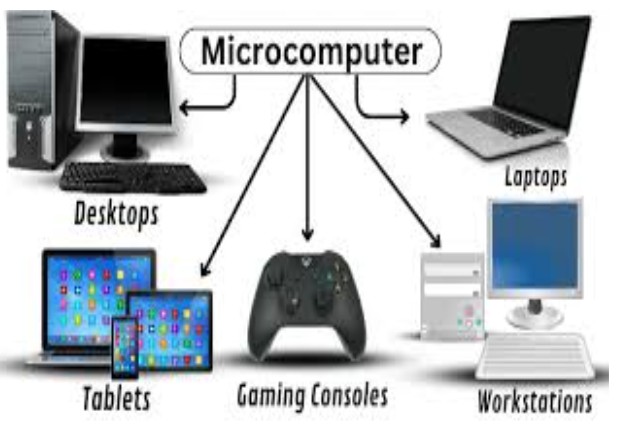
Each type of computer meets different needs and is optimized for specific tasks based on its size and processing capabilities.
Based on Operation (Analog, Digital, Hybrid)
Computers can be categorized into three main types based on their processing methods: analog, digital, and hybrid computers. Each type has different features and is suitable for different tasks.
- Analog Computer:
- Functionality: Analog computers process continuous data and are mainly used to mimic physical systems.
- Applications: Commonly used in flight simulators, weather forecasting, and other fields where real-time data is important. They excel in solving differential equations and modeling dynamic systems. - Digital Computer:
- Functionality: Digital computers work using discrete values (binary data). They perform calculations and data processing through a defined sequence of steps and algorithms.
- Applications: The most common type of computers today, used in personal computers, servers, smartphones, and embedded systems. They are well suited for data analysis, software applications, and internet browsing. - Hybrid Computer:
- Functionality: Hybrid computers combine features of both analog and digital computers. They use the precision and control of digital systems while processing continuous data with analog speed.
- Applications: Used in specialized fields such as medical imaging, industrial process control, and simulation tasks where complex calculations involving both continuous and discrete data are required.



Each type of computer has its own strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for specific applications depending on the requirements.
Based on Usage (Desktop, Laptop, Tablet, Smartphone)
As of May 2025, the usage share of different device categories with various operating systems is as follows:
- Smartphone:
- Android holds a significant lead with about 72% market share.
- Apple's iOS accounts for approximately 28% of the smartphone market. - Desktop and Laptop:
- Microsoft Windows dominates this category with about 71% market share.
- The remaining percentage is covered by other operating systems like macOS and various Linux distributions. - Internet Traffic:
- Mobile devices contribute significantly to internet traffic, with mobile phones accounting for 96.3%, and smartphones alone making up 94.2% of that traffic.
- In contrast, laptops and desktops account for about 61.5% of internet traffic.



These statistics highlight the growing dominance of mobile devices in both market share and internet usage compared to traditional desktop and laptop computers.